Overview:-
Contusions are one of the most well-known types of Injuries happening in dynamic kids.
A contusion, or bruise, is brought about by a hard impact to the body that can make harm the outside of the skin and to more profound tissues also relying upon the severity of the blow. Let’s Discuss more about it in the Article below:-
What is Contusion?
A contusion is medical terminology for a bruise. This condition appears when the blood vessels are injured and start bleeding under the skin after a hard bump, but the skin does not rip.
The bump causes the blood to flow out of damaged blood vessels into the neighbouring tissues; because of the internal bleeding, the area may swell and look red or blue.
A contusion may be painful when touched because the blood pooled under the skin puts pressure on nearby nerve endings. Some types of contusion are mentioned below.
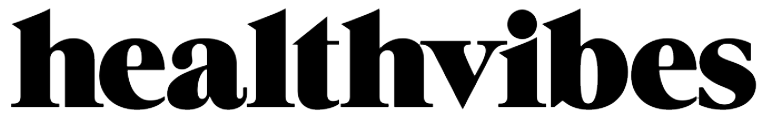
Subcutaneous contusion – This contusion appears just below the skin and is the most common kind of contusion. Small blood vessel injuries under the skin of some exposed areas cause most subcutaneous discolorations, such as the elbow or knee.
Sometimes, a large bruise often causes massive bleeding from a vein or artery, which is difficult to stop. These discolorations are large and extremely painful, and they are usually due to significant wounds, such as a severe car accident.
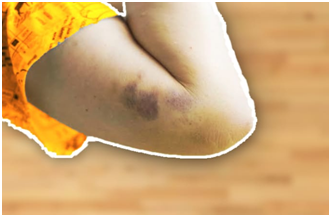
Eye contusion – This type of contusion appears on or around the eye. Discolorations on the eyelid can be painful and may look swollen. The cornea may also get damaged; this can be more serious, especially without treatment or other eye injuries.
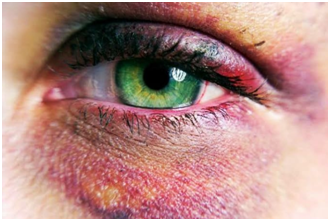
Cartilage contusion – A cartilage is a rigid but elastic connective tissue that can withstand significant pressure. The outside of the ears (pinna) and the tip of the nose both comprise of cartilage. A contusion can occur on cartilage when it bends or something sharp hits the cartilage. Most cartilage injuries are not severe and will heal without treatment.
- Pain increases when you touch the area around the bruise
- Red, blue, or black skin may change to green or yellow after some time
- Feel stiffness while moving the bruised area of your body
What causes contusion?
- Bleeding disorders such as Hemophilia make you bruise or bleed more easily
- Kidney or liver illness, or an injury
- Medications such as blood thinners and herbal medicines
- Old and weakened skin and muscles because of poor nutrition
How to prevent a contusion?
- Perform stretching exercises before playing sports.
- Wear protective equipment when you play sports.
- Give your body breaks, do not continuously perform activities, or play for too long.
How is a contusion diagnosed?
For a contusion to be diagnosed, you may need any of the following tests:
- Blood Tests – These tests are performed to check for any blood disorders such as hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease. It tells how long it takes for your blood to clot.
- Ultrasound – These pictures tell how deep the bruise is and if your organs, such as your liver or kidney, are injured.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – MRI pictures show if hematoma has begun to form.
How is contusion treated?
In most of the cases, bruises recover without taking any treatment. The treatments depend on the body part that is injured and how severe it is. Some of the treatments are mentioned below.
- Aspiration – it is a process that drains pooled blood in your muscle. This helps to prevent increased pressure in the muscle.
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) – NSAIDs such as ibuprofen help to decrease pain and swelling.
- Surgery – in sporadic cases, you may undergo surgery to restore a muscle injury or relieve pressure in the muscle caused by swelling.
Home treatment
- Relaxing the injured areas will help you keep weight off your injured part.
- Applying ice will help you to decrease swelling and pain and will also restrict tissue damage.
- Compress the injured area – Use a band-aid to cover the injured area. Wrap a band-aid around the area over the bruised muscle. Make sure the dressing is not too tight.
- Rising the injured area above the heart level helps you to get rid of the swelling and pain. You may use pillows and blankets to elevate the area.
Sources:-
Healthvibes has strict sourcing guidelines and relies only on academic research institutions and medical associations. We do not use tertiary references. You can read our editorial policy.
- Bone bruise. (n.d.).
urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=134&contentid=514 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Bruise: First aid.
mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-bruise/basics/art-20056663 - What is a bone bruise? (n.d.).
saintlukeskc.org/health-library/bone-bruise